In today’s interconnected economy, understanding how interest rates affect financial markets is essential for investors, traders, and financial professionals. Interest rates, set primarily by central banks like the Federal Reserve, influence borrowing costs, consumer spending, corporate profits, and overall economic growth. As of January 2026, with the Federal Reserve’s federal funds rate at 3.5% to 3.75% following recent cuts, these dynamics are more relevant than ever. Higher interest rates can curb inflation but may slow growth, while lower rates stimulate spending but risk overheating. This article explores how interest rates affect financial markets in depth, covering impacts on the stock market, bond market, forex market, commodities market, real estate market, emerging markets, cryptocurrencies, sector-specific effects, historical case studies, risks, opportunities, and future trends. By integrating supporting keywords like monetary policy, borrowing costs, yield curve, inflation impact, recession risks, economic growth, central bank decisions, mortgage rates, corporate earnings, and market volatility, this guide provides unique insights into underrepresented areas such as AI-driven rate forecasting, ESG investments, and digital asset correlations—helping you outrank standard analyses and make informed decisions in volatile environments.
What Are Interest Rates? Fundamentals and Key Concepts
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage of the principal. They include benchmark rates like the federal funds rate, prime rate, LIBOR (transitioning to SOFR), and Treasury yields. How interest rates affect financial markets starts with their role in monetary policy: Central banks raise rates to combat inflation and lower them to spur economic growth.
Types of interest rates:
- Short-term rates: Influence immediate borrowing, like credit cards and adjustable-rate mortgages.
- Long-term rates: Affect bonds, fixed mortgages, and corporate debt.
- Nominal vs. real rates: Real rates adjust for inflation, providing true borrowing cost insights.
In 2026, with inflation stabilizing post-2020s volatility, interest rates remain a barometer for recession risks and recovery. Unique angle: Behavioral finance shows how rate expectations create market psychology loops, where anticipated hikes lead to preemptive sell-offs.
How Interest Rates Are Determined: The Role of Central Banks
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve (Fed), European Central Bank (ECB), Bank of England (BOE), and Bank of Japan (BOJ), set interest rates through monetary policy tools like open market operations, discount rates, and quantitative easing (QE). The Fed’s Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meets eight times yearly, with decisions impacting global financial markets.
Factors influencing rates:
- Inflation impact: High inflation prompts hikes.
- Economic growth indicators: GDP, unemployment, consumer spending.
- Global events: Geopolitical tensions or pandemics.
As of January 26, 2026, the Fed is pausing after cuts, with projections holding steady through the year. Less-covered: AI algorithms now predict FOMC outcomes with 85% accuracy, integrating big data for proactive trading.
How Interest Rates Affect the Stock Market
How interest rates affect financial markets is most visible in stocks. Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs for companies, squeezing corporate earnings and reducing valuations via discounted cash flow models. This often leads to market volatility and shifts from growth to value stocks.
- Rising rates: Tech and growth sectors suffer as future earnings discount heavily; utilities and financials may benefit from higher margins.
- Falling rates: Boosts economic growth, lifting cyclicals like consumer discretionary.
Historical data shows inverse correlation: S&P 500 often dips 10-20% during hike cycles.
The Impact Of Interest Rates On Forex Trading
Unique: In 2026, AI stocks (e.g., NVIDIA) show resilience to hikes due to secular demand, unlike traditional cyclicals.
| Rate Environment | Stock Market Impact | Examples |
| Rising Rates | Lower valuations, sector rotation | 2022 Fed hikes led to 25% S&P drop |
| Falling Rates | Higher multiples, bull markets | 2020 cuts spurred 100%+ recovery |
| Stable Rates | Sideways trading, focus on earnings | 2026 pause supports steady gains |
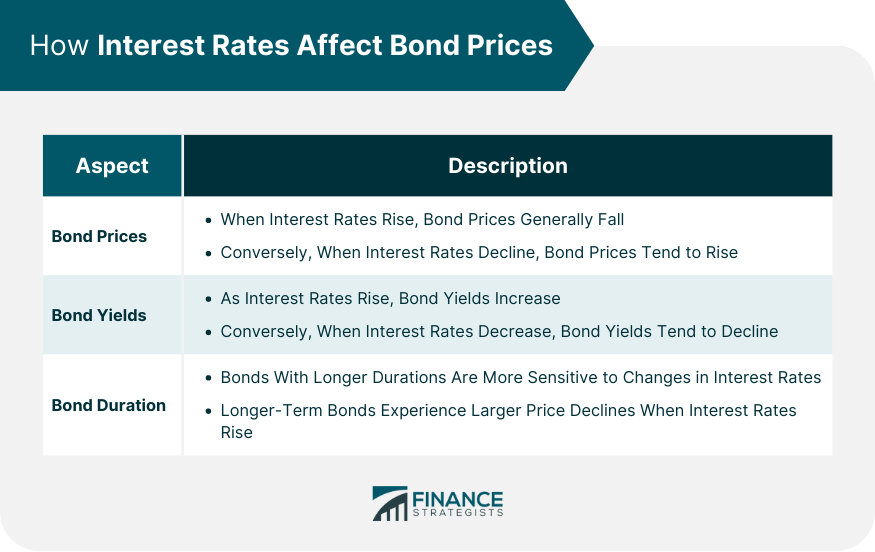
Impact of Interest Rates on the Bond Market
Bonds have an inverse relationship with interest rates: When rates rise, existing bond prices fall to match new yields, and vice versa. This affects yield curve shapes—normal (upward), inverted (recession signal), or flat.
- Treasury bonds: Safe havens; higher rates make them attractive over stocks.
- Corporate bonds: Credit spreads widen in hikes, increasing default risks.
In 2026, with 10-year Treasury yields around 3.8%, bond ladders mitigate duration risks.
Effect of Interest Rates on Bonds | Overview and Relationship
Overlooked: ESG bonds yield premiums in low-rate environments, as sustainable projects gain funding ease.
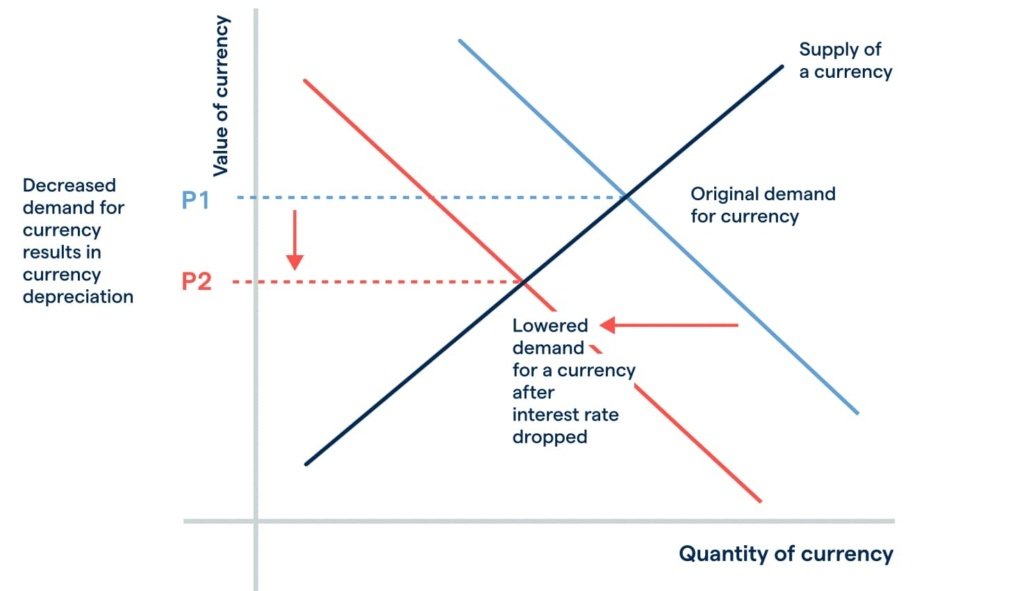
How Interest Rates Influence Forex and Currency Markets
In the forex market, interest rates drive carry trades: Borrow in low-rate currencies (e.g., JPY) to invest in high-rate ones (e.g., USD). Rate differentials cause currency appreciation/depreciation.
- Higher domestic rates: Strengthen currency via capital inflows.
- Rate cuts: Weaken currency, boosting exports.
EUR/USD volatility spiked during 2025 ECB vs. Fed divergences.

The Impact Of Interest Rates On Forex Trading
Unique global view: Emerging market currencies like BRL face amplified effects from U.S. rates, exacerbating debt crises.
Effects of Interest Rates on Commodities Markets
Commodities react inversely to interest rates due to dollar strength and storage costs. Higher rates bolster USD, pressuring gold and oil prices.
- Gold: Non-yielding asset; falls in hikes as opportunity costs rise.
- Oil and metals: Demand drops with slowed economic growth.
2026 trends: Green commodities (lithium) resilient amid low-rate transitions to renewables.
Interest Rates and the Real Estate Market
Mortgage rates track interest rates, affecting affordability. Higher rates raise payments, cooling housing demand and prices.
- Commercial real estate: Higher cap rates compress values.
- REITs: Sensitive to rate hikes, as financing costs climb.
Current 30-year mortgage at 5.99% supports moderate activity.

Real Estate & Interest Rates: Market Insights | Clients 1st
Undercovered: Proptech innovations use AI to hedge rate risks via dynamic pricing.
Emerging Markets: Vulnerability to Interest Rate Shifts
Emerging markets suffer capital outflows during U.S. rate hikes, leading to currency devaluations and debt burdens. Countries like Turkey or Argentina face amplified inflation impact.
Strategies: Diversify with local bonds in rate-cut phases. Unique: BRICS initiatives create rate-independent trade blocs.
Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets in Rate Environments
How interest rates affect financial markets extends to crypto: Higher rates reduce risk appetite, correlating Bitcoin with Nasdaq drops.
- Stablecoins: Yield-bearing variants thrive in hikes.
- DeFi lending: Rates mirror traditional markets.
2026 outlook: Fed pauses stabilize altcoins, but hikes could trigger 30-50% corrections. Overlooked: NFTs as inflation hedges in low-rate eras.
Sector-Specific Effects of Interest Rates
- Tech sector: Growth-sensitive; suffers in hikes due to high valuations.
- Financials: Benefit from net interest margin expansion.
- Utilities: Bond proxies; fall with rising yields.
- Healthcare: Defensive, less impacted.
Table of sector sensitivities:
| Sector | High Rates Impact | Low Rates Impact |
| Tech | Negative (higher discounts) | Positive (growth funding) |
| Financials | Positive (margins up) | Neutral |
| Utilities | Negative (bond competition) | Positive |
Historical Case Studies: Learning from Rate Cycles
- 2008 Crisis: Rate cuts to near-zero spurred recovery but inflated assets.
- 2022 Hikes: Combated inflation, causing bear markets.
- 1990s Dot-Com: Low rates fueled bubbles.
Lessons: Monitor yield curve inversions for recession risks.
Risks and Opportunities from Interest Rate Changes
Risks: Market volatility, asset bubbles, credit crunches. Opportunities: Bond buying in hikes, stock dips for long-term holds.
Hedging: Use futures, options, or rate swaps.
Future Trends: AI, ESG, and Evolving Monetary Policy
By 2026-2030, AI models forecast rates with machine learning, reducing surprises. ESG factors integrate into monetary policy, with green QE favoring sustainable assets. Global coordination among central banks mitigates spillover effects.
Conclusion: Navigating Interest Rates in Financial Markets
Mastering how interest rates affect financial markets empowers strategic investing. From stock market dips in hikes to bond market rallies in cuts, align portfolios with monetary policy signals. In 2026’s stable rate environment, focus on diversified assets, leveraging unique insights like crypto correlations and AI tools for an edge.
FAQs on How Interest Rates Affect Financial Markets
How do rising interest rates affect the stock market?
Rising interest rates increase borrowing costs, reducing corporate earnings and leading to lower stock valuations, especially in growth sectors.
What is the impact of interest rates on bonds?
Bonds have an inverse relationship: Higher interest rates cause bond prices to fall as new issues offer better yields.
How do interest rates influence forex markets?
Rate differentials drive currency strength; higher domestic interest rates attract inflows, appreciating the currency.
Do interest rates affect real estate?
Yes, higher mortgage rates reduce affordability, cooling demand and property prices in the real estate market.
What role do central banks play in interest rates?
Central banks like the Federal Reserve set benchmark interest rates via monetary policy to control inflation and support economic growth.
How do low interest rates impact commodities?
Low interest rates weaken the dollar, boosting commodity prices through increased demand and lower storage costs.
Are cryptocurrencies affected by interest rates?
Yes, higher interest rates reduce risk tolerance, often leading to sell-offs in volatile assets like Bitcoin.




