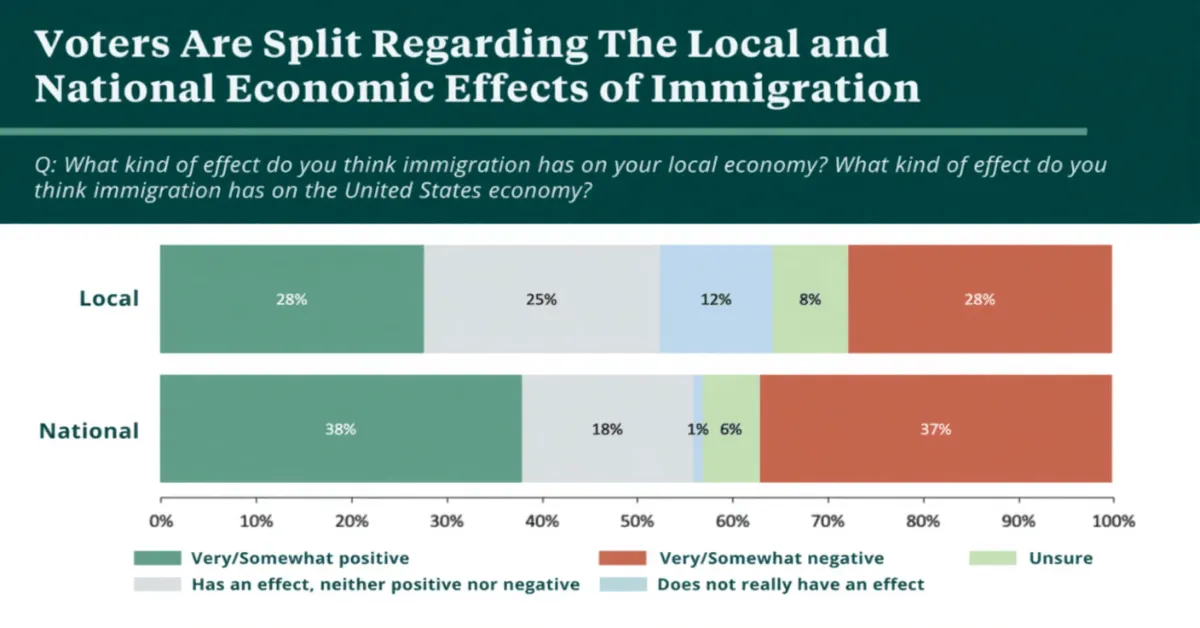
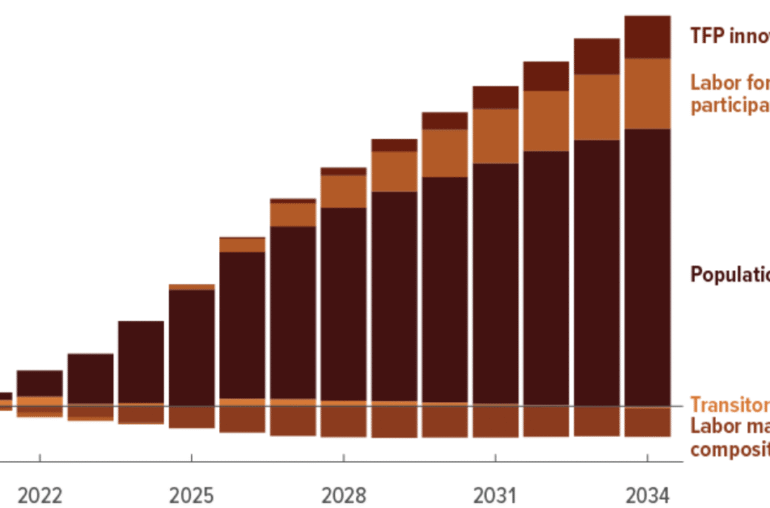
Immigration is one of the most debated economic topics in the world. Yet when economists analyze data instead of opinions, a clear picture emerges. Understanding how does immigration help the economy requires looking at labor markets, productivity, innovation, public finances, and long-term growth.
Immigrants are not just workers crossing borders. They are consumers, taxpayers, entrepreneurs, and contributors to economic expansion. In both developed and developing countries, immigration plays a measurable role in strengthening economic performance.
This article explains how immigration helps the economy, using economic mechanisms that governments, researchers, and institutions rely on.
What Is Immigration in Economic Terms?
From an economic perspective, immigration is the movement of people across borders to live and work in another country. When immigrants enter an economy, they immediately interact with key economic systems:
- Labor markets
- Consumer demand
- Tax systems
- Housing and services
- Innovation and entrepreneurship
This interaction is the foundation of how immigration helps the economy.
How Does Immigration Help the Economy?
Immigration helps the economy through multiple direct and indirect channels. Below are the most important and evidence-based ways immigration contributes to economic growth.
1. Immigration Expands the Labor Force
One of the clearest answers to how does immigration help the economy is labor force expansion.
Immigrants increase the number of working-age people, which:
- Fills labor shortages
- Supports industries facing worker gaps
- Keeps businesses productive
Many economies face aging populations and declining birth rates. Immigration helps maintain a stable workforce and prevents labor market contraction.
2. Immigration Increases Economic Output (GDP)
More workers and more consumers lead to higher economic output.
Immigration contributes to:
- Increased production of goods and services
- Higher national income
- Stronger GDP growth
Studies consistently show that countries with higher immigration levels experience faster economic growth over time.
3. Immigration Raises Productivity Levels
Immigration does not just add workers. It improves productivity.
Immigrants often:
- Bring new skills
- Complement native workers
- Increase specialization
When labor becomes more specialized, overall efficiency improves. This is a key reason how immigration helps the economy beyond simple job creation.
4. Immigration Supports Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Immigrants are statistically more likely to start businesses than native-born citizens.
They contribute to:
- Startup creation
- Technological innovation
- Business expansion
Many high-growth companies were founded or co-founded by immigrants. Institutions like Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development consistently highlight immigration’s role in innovation-driven economies.
5. Immigration Strengthens Public Finances
A common misconception is that immigrants are a fiscal burden. In reality, immigration often strengthens government finances.
Immigrants:
- Pay income and consumption taxes
- Contribute to social security systems
- Support pension systems in aging societies
Over the long term, immigrants often contribute more in taxes than they receive in benefits, especially when immigration policies favor working-age individuals.
6. Immigration Helps Address Aging Populations
Many developed economies face demographic decline.
Immigration helps by:
- Increasing the working-age population
- Supporting retirees through tax contributions
- Stabilizing dependency ratios
Without immigration, many economies would struggle to fund pensions and healthcare systems.
7. Immigration Boosts Consumer Demand
Immigrants are consumers as well as workers.
They spend money on:
- Housing
- Food and services
- Transportation
- Education
This increase in demand stimulates local businesses and supports job creation, reinforcing how immigration helps the economy at the community level.
8. Immigration Improves Labor Market Flexibility
Immigrants often take jobs that are hard to fill, seasonal, or location-specific.
This flexibility:
- Keeps industries running smoothly
- Reduces production bottlenecks
- Stabilizes wages over time
Sectors like agriculture, healthcare, construction, and technology heavily rely on immigrant labor.
9. Immigration Encourages Global Trade and Investment
Immigrants maintain economic links with their home countries.
These links:
- Increase international trade
- Encourage foreign direct investment
- Strengthen global supply chains
Organizations such as the World Bank recognize migration as a driver of global economic integration.
10. Immigration Helps Regional and Local Economies
At the local level, immigration:
- Revitalizes declining regions
- Increases housing demand
- Supports small businesses
Many cities experiencing population decline have stabilized or grown due to immigration-driven economic activity.
How Immigration Affects Wages and Employment
A critical part of how immigration helps the economy is understanding wage impact.
Most research shows:
- Minimal negative impact on native wages
- Positive wage effects in the long term
- Productivity gains offset labor competition
Immigration tends to complement rather than replace native workers.
Immigration and Economic Growth in Developing Countries
Immigration also benefits developing economies by:
- Increasing remittances
- Transferring skills and knowledge
- Strengthening human capital
Remittances sent back home support education, healthcare, and investment.
Role of Government Policy in Maximizing Economic Benefits
The economic impact of immigration depends heavily on policy design.
Effective immigration policies focus on:
- Labor market needs
- Skills matching
- Integration programs
- Legal work pathways
Institutions like the International Monetary Fund emphasize that well-managed immigration maximizes economic gains.
Advantages of Immigration for the Economy
- Higher economic growth
- Increased productivity
- Stronger public finances
- Greater innovation
- Labor market stability
These benefits explain how immigration helps the economy across different regions.
Potential Economic Challenges of Immigration
While beneficial overall, challenges exist:
- Short-term infrastructure pressure
- Housing demand increases
- Integration costs
These are policy challenges, not economic failures of immigration itself.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does immigration help the economy grow?
By expanding the workforce, increasing productivity, and boosting consumer demand.
Does immigration increase unemployment?
Most evidence shows little to no long-term increase in unemployment.
Do immigrants pay more taxes than they receive?
In many countries, yes, especially over the long term.
Final Conclusion
So, how does immigration help the economy?
Immigration fuels labor markets, drives innovation, strengthens public finances, supports aging populations, and increases economic growth. When managed effectively, immigration is not a burden but a powerful economic asset.
Economies that understand and harness immigration benefits position themselves for long-term stability and prosperity.