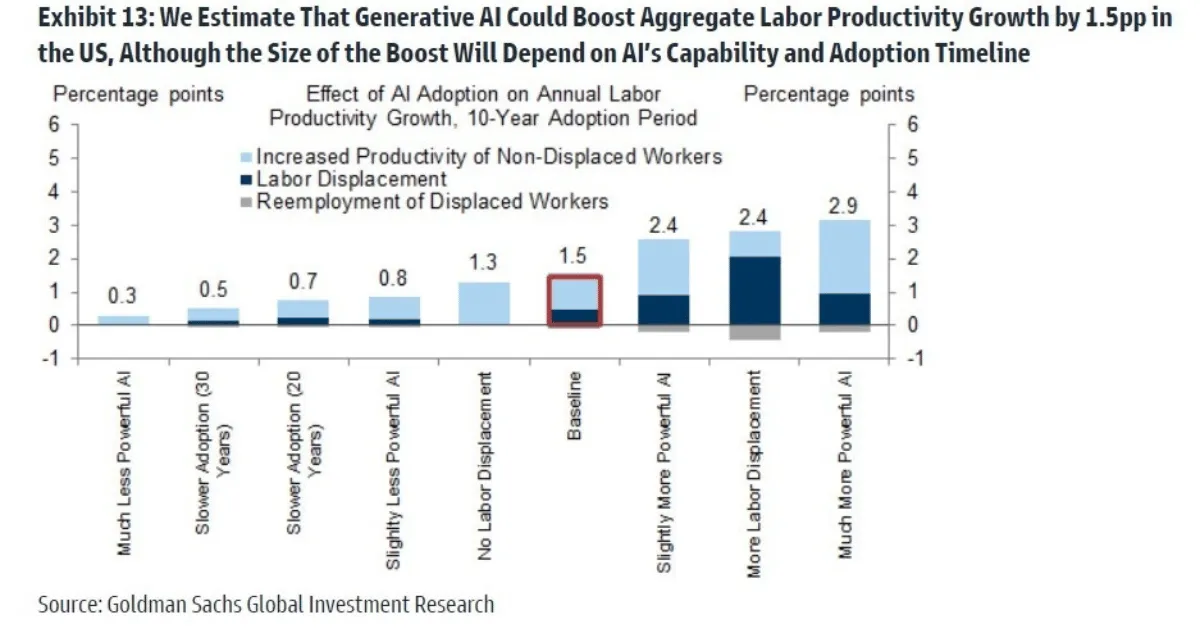
Productivity growth has long been the most important driver of rising living standards in the United States. For years, productivity gains slowed, raising concerns about long-term economic growth. Today, artificial intelligence is reshaping that trajectory. Understanding how AI is changing productivity in the US economy requires looking beyond headlines and into how firms, workers, and capital are actually reorganizing around intelligent systems.
AI is not just automating tasks. It is changing how output is produced, how decisions are made, and how efficiently resources are allocated. This article explains how AI is changing productivity in the US economy, using real economic mechanisms, sector-level impacts, and insights most competitors overlook.
What Productivity Means in the US Economy
In economic terms, productivity measures how much output is produced per unit of input.
Key productivity concepts include:
- Labor productivity: output per hour worked
- Total factor productivity (TFP): efficiency gains beyond labor and capital
- Firm-level productivity: how efficiently individual companies operate
When productivity rises, wages can grow without causing inflation, profits increase, and overall economic output expands. This is why productivity sits at the center of how AI is changing productivity in the US economy.
Why Productivity Growth Matters More Than Ever
The US economy faces structural challenges:
- Aging workforce
- Slower labor force growth
- Rising global competition
- Higher fiscal pressure
Without productivity growth, long-term economic expansion stalls. AI offers a rare opportunity to break that constraint by increasing output without proportional increases in labor or capital.
How AI Is Changing Productivity in the US Economy: Core Channels
AI impacts productivity through multiple transmission channels. Let’s break them down.
1. AI Automates Routine and Cognitive Tasks
Earlier waves of automation focused on physical labor. AI targets cognitive work.
AI increases productivity by automating:
- Data entry and processing
- Scheduling and coordination
- Document review and analysis
- Customer service interactions
This frees workers to focus on higher-value tasks, raising output per hour worked. This task reallocation is a primary reason how AI is changing productivity in the US economy.
2. AI Improves Decision-Making Quality
Poor decisions reduce productivity.
AI enhances productivity by:
- Analyzing large datasets instantly
- Identifying optimal choices
- Reducing human bias and error
- Improving forecasting accuracy
Better decisions at scale compound across firms and industries, producing economy-wide productivity gains.
3. AI Raises Total Factor Productivity
Unlike basic automation, AI improves how inputs are combined.
AI increases TFP by:
- Optimizing workflows
- Reducing waste
- Improving coordination across departments
- Enhancing supply chain efficiency
These gains show up as higher output without additional labor or capital, the purest form of productivity growth.
4. AI Is Reshaping Firm-Level Productivity in the US
Productivity gains are uneven across firms.
High-performing US firms use AI to:
- Scale operations rapidly
- Operate with leaner teams
- Optimize pricing and inventory
- Improve customer targeting
Less adaptive firms lag behind. This widening productivity gap is a defining feature of how AI is changing productivity in the US economy.
Sector-Level Impact: Where AI Is Driving Productivity Gains
To understand the full picture, we need to examine specific sectors.
AI in Manufacturing Productivity
AI improves manufacturing productivity through:
- Predictive maintenance
- Quality control automation
- Robotics coordination
- Supply chain optimization
US manufacturers using AI produce more with fewer downtime disruptions and lower defect rates.
AI in Professional and Business Services
Services make up the majority of the US economy.
AI increases productivity in services by:
- Automating research and analysis
- Enhancing project management
- Supporting decision-making
This is especially impactful because service productivity has historically been difficult to improve.
AI in Healthcare Productivity
Healthcare productivity gains were once limited.
AI improves productivity by:
- Assisting diagnostics
- Reducing administrative burden
- Optimizing scheduling and resource use
These gains help control costs while improving outcomes.
AI in Finance and Insurance
Financial services benefit heavily from AI.
AI boosts productivity through:
- Automated risk assessment
- Fraud detection
- Compliance automation
- Faster transaction processing
Institutions like JPMorgan Chase deploy AI to improve both front-office and back-office efficiency.
AI in Retail and Logistics
AI drives productivity by:
- Improving demand forecasting
- Optimizing inventory
- Enhancing route planning
- Reducing fulfillment errors
These gains ripple across supply chains nationwide.
AI, Labor Productivity, and the US Workforce
A key concern is how AI affects workers.
AI increases labor productivity by:
- Augmenting human capabilities
- Reducing time spent on low-value tasks
- Enabling one worker to manage more output
Rather than replacing most workers, AI changes how productive each worker can be.
Wages, Productivity, and Income Effects
Historically, productivity growth supports wage growth.
AI-driven productivity can:
- Raise wages for AI-complementary roles
- Increase returns to skills and education
- Pressure routine middle-skill jobs
This uneven impact explains why how AI is changing productivity in the US economy is closely tied to inequality and workforce policy.
The AI Productivity Paradox in the US
Despite heavy investment, productivity gains initially appeared modest. This is known as the AI productivity paradox.
Key reasons include:
- Learning and adoption delays
- Poor management integration
- Organizational resistance
- Skills mismatches
Productivity gains accelerate only after firms restructure workflows around AI, not just add tools.
Why the US Is Uniquely Positioned for AI-Driven Productivity
The US has structural advantages:
- Deep capital markets
- Leading AI research institutions
- Strong entrepreneurial ecosystem
- Flexible labor markets
Organizations like National Science Foundation support foundational AI research that feeds long-term productivity growth.
Investment, Capital Deepening, and AI
AI drives a new wave of capital investment.
This includes:
- Cloud infrastructure
- Data centers
- Software platforms
Capital deepening combined with AI raises productivity more sustainably than labor expansion alone.
Diffusion: Why AI Productivity Gains Take Time
AI does not raise productivity instantly.
Diffusion depends on:
- Firm size
- Management quality
- Worker skills
- Access to data
Large US firms adopt faster, while small firms lag. Bridging this gap is critical to broad productivity growth.
Risks and Constraints on Productivity Gains
Understanding how AI is changing productivity in the US economy also means recognizing limits.
Key Constraints
- Skills shortages
- Data quality issues
- Over-automation risks
- Regulatory uncertainty
Poor implementation can even reduce productivity in the short term.
Long-Term Outlook for US Productivity Growth
Most economists expect:
- Gradual acceleration in productivity
- Stronger gains as AI diffusion improves
- Higher long-run potential GDP
AI’s productivity impact is cumulative, not explosive.
What Most Articles Get Wrong
Most content fails because it:
- Treats AI as instant productivity
- Ignores organizational change
- Confuses automation with productivity
- Avoids discussing diffusion lag
Productivity is about systems, not tools.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does AI improve productivity in the US economy?
By automating tasks, improving decisions, and increasing efficiency across industries.
Will AI lead to higher wages?
For many workers, yes, especially those whose skills complement AI.
Is AI productivity growth already visible?
Yes, but unevenly across firms and sectors.
Final Conclusion
So, how AI is changing productivity in the US economy?
AI is increasing labor productivity, raising total factor productivity, reshaping firm efficiency, and unlocking new growth potential. The gains are real but uneven, gradual, and dependent on adoption, skills, and management quality.
AI is not a productivity miracle by itself.
It is a productivity multiplier when paired with the right systems.The future of US economic growth will depend not on whether AI exists, but on how well it is integrated into work, firms, and institutions.